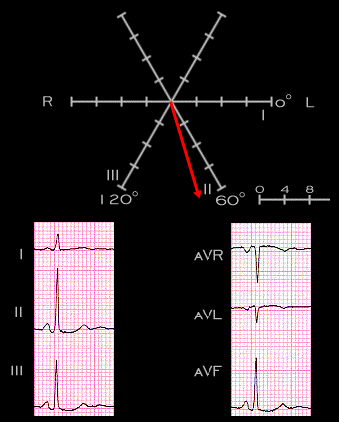
A rapid way to identify the main (and mean) electrical axis is to identify the leads having the greatest QRS net amplitude since the axis will be most nearly parallel to these leads. In this example, the QRS complex is positive in leads I,II, III and aVF and of greatest amplitude in leads II and aVF. This localizes the axis to somewhere between and on the positive side of these two leads. It is of greater amplitude in lead II than in lead aVF and therfore more parallel and closer to the lead II positive axis than to the positive axis of lead aVF. The smallest QRS amplitude is in lead I, indicating that the electrical axis is closest to perpendicular to this lead but still on the positive side. Thus, by "eye-balling" the QRS complex, it is possible to predict the electrical axis in the frontal plane with reasonable accuracy.
