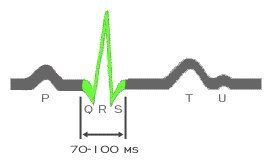
The duration of the normal QRS complex ranges between 0.08 and 0.10 seconds (80-100 ms). It tends to be longer in men than in women, reflecting the generally larger ventricular muscle mass in men. The QRS duration is shorter in children than in adults and is prolonged when there is an abnormality in intra-, or inter-ventricular conduction. The current computerized ECG machines record all leads simultaneously and and automatically measure the duration of the various waves and intervals, i.e. the P wave, and QRS complex and the RR, PR and QT intervals, on superimposed median beats from each of the simultaneously recorded leads. By so doing, it is able to identify the earliest onset and the latest offset of the various intervaals. It is important to recognize that these onset and offset points are most often found in different leads. W hen these complexes or intervals are measured manually, the lead or leads with the widest complexes or longest intervals should be chosen. This is usually lead II or V1 for the P wave, lead V1 or V2 for the QRS complex, lead II ot V1 for the PR interval and lead V2 or V3 for the QT interval. However, there is frequently no uniformity among ECG readers and some prefer to make all measurements in the same lead, usually lead II