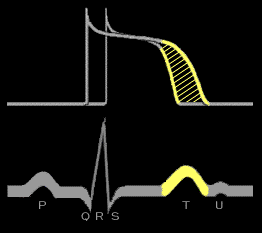
As discussed earlier , the T wave on the body surface electrocardiogram reflects the unopposed electrical forces that occur when the ventricular cells sequentially repolarize. These unopposed electrical forces result in an electrical vector that has a magnitude and direction, just as the unopposed electrical forces that occur during atrial and ventricular depolarization and cause the P wave and QRS complex have a magnitude and direction.
