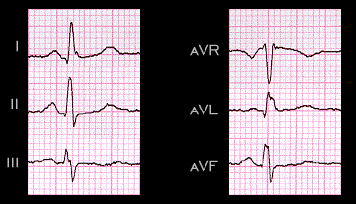
The QRS complex of this ECG has three distinctive and separable components:
1) a small, narrow initial component of about 10-20 msec consisting of the small narrow small Q wave in leads I,II,and aVL and the initial portion of the R wave in lead III
2) a middle component of about 40 ms duration consisting of the R wave in leads I,II, and aVF, the remainder of the R wave in lead III and the S wave in lead aVR
3) a terminal component of about 30 ms duration comprised of the S wave in leads II,III and aVF and the R wave in lead aVL.
