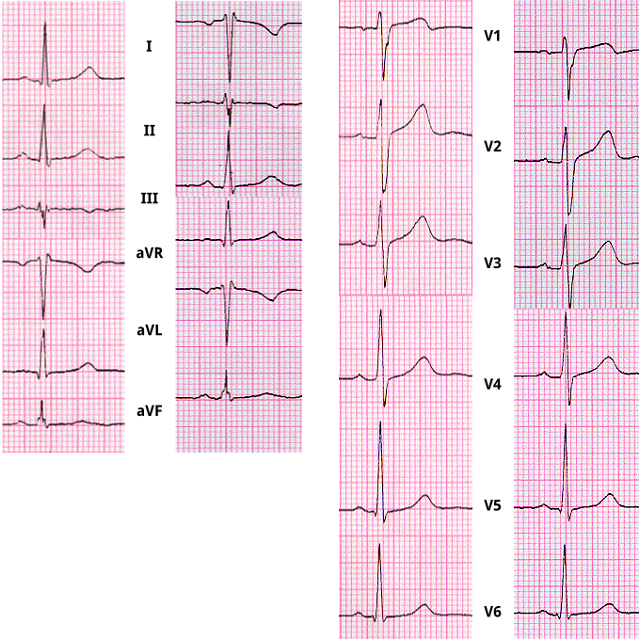
Shown here are 2 ECGs from the same patient. In each column, the tracing on the left was recorded with the leads correctly applied, while the tracing on the right was recorded with the right and left arm leads reversed. Although then entire waveform is involved, focus on the P waves.
In the limb leads, the P wave becomes inverted in leads I and aVL and flat or isoelectric in leads II and aVR. when he left and right arfm leads afe reversed. Note also that leads II and III are reversed as are leads aVR and aVL but that lead aVF is unchanged.
In the chest leads, the P wave (as well as the QRS complex and T wave) remains normal and unchanged because the exploring, or positive electrode is normally placed and the indifferent electrode, also referred to as the central terminal, is constructed by combining the three limb leads (see 1.9.17), and is not affected by the arm lead reversal.