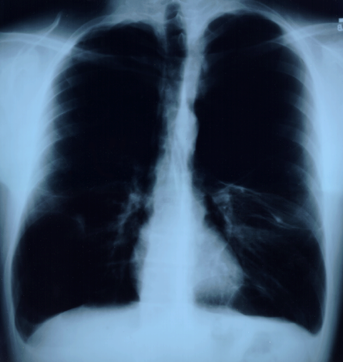
This P wave configuration is often interpreted as indicating right atrial enlargement or hypertrophy and this may be a contributing factor. More likely, however, it reflects the vertical position of the heart which occurs because the diaphragms in patients with severe obstructive airway disease are characteristically depressed and flattened. The posterior-anterior (PA) chest x-ray shown here is from such a patient.
