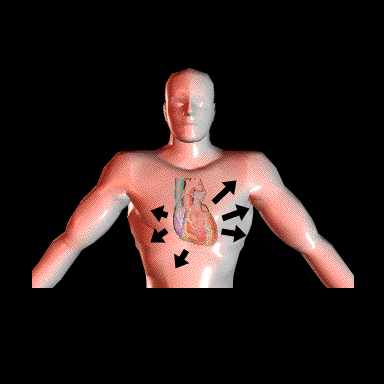
In the intact heart, there are simultaneously occurring electrical forces that are directed anteriorly and posteriorly, superiorly and inferiorly and to the right and to the left. However, these forces are of unequal magnitude because of the unequal myocardial muscle mass in the two ventricles. The signal recorded by either a unipolar or bipolar electrode placed on the body surface will reflect the location of the lead on the body surface and the direction of the uncancelled or resultant electrical forces.
