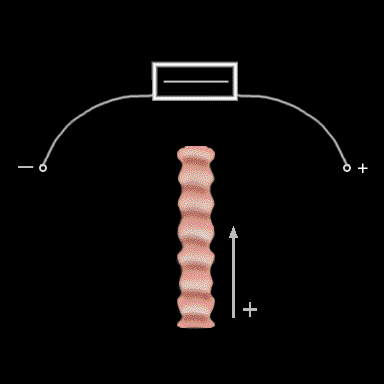
Impulses approaching the electrode from a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the electrode pair will not cause a deflection since the positive and negative components of the signal will be equal in strength and direction and will cancel each other.
