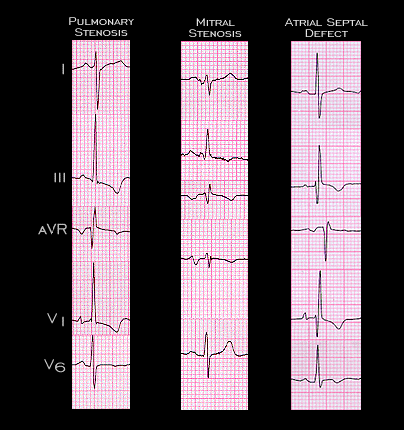
Thus far, we have considered the three more or less distinct electrocardiographic manifestations of right ventricular hypertrophy and/or dilatation. These are reviewed here and include: 1) right ventricular systolic pressure overload such as that caused by severe pulmonary hypertension or pulmonic valvular (or subvalvular) stenosis. 2) Mild to moderate pulmonary (and right ventricular) hypertension due to mitral stenosis or other cause of obstruction at the level of the mitral valve. 3) Right ventricular volume overload such as that caused by an atrial septal defect. The final types of electrocardiographic change are those that accompany chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD) i.e. chronic cor pulmonale, and those that accompany an acute pulmonary embolus, i.e. acute cor pulmonale
