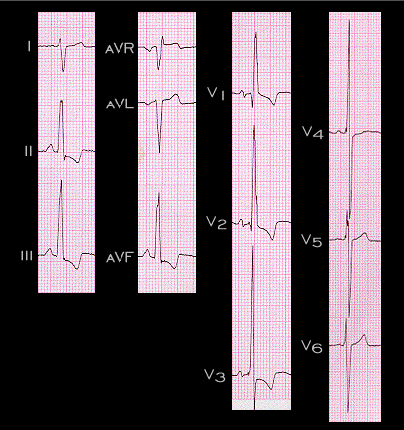
When pulmonary hypertension does occur in the patient with an atrial septal defect, the ECG reflects the increasing pressure overload of the right ventricle. The ECG shown here is from a 31 year old male with a large atrial septal defect and pulmonary hypertension. The QRS complex is 0.12 seconds in duration and is slightly notched (seen best in lead V2) with features of right bundle branch block. In this tracing, the main QRS axis in the frontal plane is directed to the right (+120 degrees), the amplitudes of the RR’ wave in V1 and the S wave in V6 are increased and the R to S ratio in V6 is less than 1. This tracing is quite similar to that of the patient with stenosis of the pulmonary valve shown earlier (page 4.2.8)
