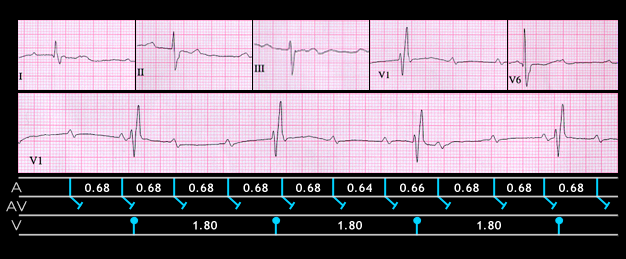
In elderly patients who not receiving drugs that affect the AV node, complete AV block is frequently caused by fibrosis or calcification extending into the AV conduction system. This is known as Lev’s disease or Lenegre’s disease (it was described independently by both). The ECG shown here is from an 84 year old male. It shows complete AV block and AV dissociation. The sinus P waves have a rate of 100 (PP interval = 0.60 seconds) and the ventricular rate is 33 (RR interval = 1.80 seconds) The QRS duration is prolonged (0.15 seconds) and the wave form suggests right bundle branch block with left anterior fascicular block. These findings suggests the following:
- that there is diffuse conducting system disease,
- that the block is distal to the AV node and
- that the escape pacemaker is located below the His bifurcation.
An alternative but less likely explanation is that there was a pre-existing IV conduction disturbance causing the right bundle branch and left anterior fascicular block and that the site of block was within the AV node.
