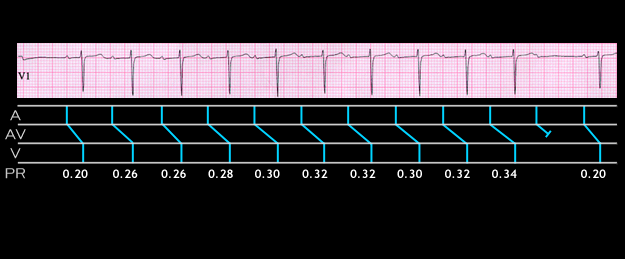
This ECG is another example of type 1 2nd degree AV block, but here, the P:QRS ratio is 11:10. Note that the PR interval,shown below the ladder diagram, initially increases from 0.20 to 0.26 seconds, an increment of 0.06 seconds. Thereafter, it increments by no more than 0.02 seconds. This is the typical Wenckebach structure.
