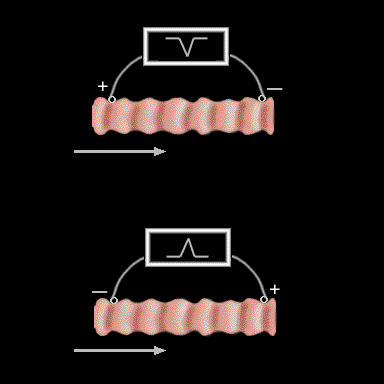
When the two unipolar electrodes are connected to form a single bipolar electrode, the polarity of the wave form will be determined by which of the individual unipolar electrodes is subtracted from the other. For instance, if the signal from the electrode on the right is subtracted from the signal from the electrode on the left, the resulting signal will be negative. If the order is reversed, then the resulting signal will be positive. Stated another way, if the positive pole is on the side towards which the impulse is traveling, the signal will be positive. If the positive pole is away from the direction of the impulse, the signal will be negative.
