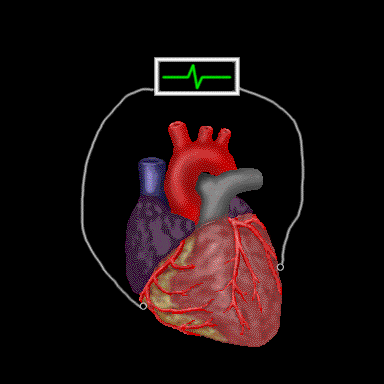
Electrical activity in individual fibers and/or the entire heart can be recorded by two extracellular electrodes of opposite polarity (one positive, the other negative) placed on the surface of individual fibers, or on the surface of the heart. The wave form recorded as the cells sequentially depolarize and then sequentially repolarize is an extracellular electrogram.
