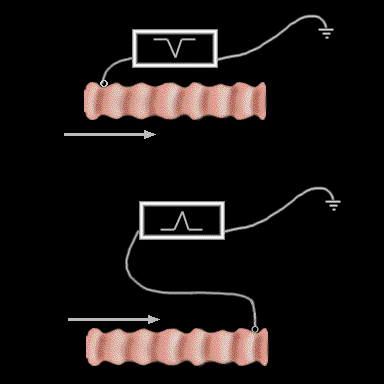
A bipolar electrode consists of two unipolar electrodes which are connected. The wave form is generated by subtracting the output of one of the unipolar leads from the output of the other. In the example shown here, the signal recorded when the unipolar recording electrode located on the left side of the fiber will be negative as the impulse passes away from it, whereas the signal recorded when the recording electrode is placed on theright side of the fiber will be positive as the impulse moves towards it.
