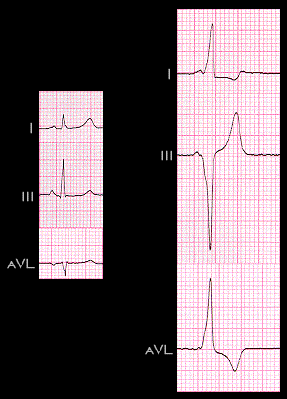
This is another example of a secondary T wave abnormality. In the tracing on the left, the PR interval, QRS complex and T wave are each normal. The tracing on the right, recorded from the same patient, shows ventricular pre-excitation, with a short PR interval and the changes in the shape and duration of the QRS complex that reflect the changes in the sequence of depolarization and changes in the shape ot the T wave. As in the patient with left bundle branch block shown on the preceding page, these T wave changes reflect the changes in the sequence of repolarization that are the necessary result of the changes in the sequence of depolarization
