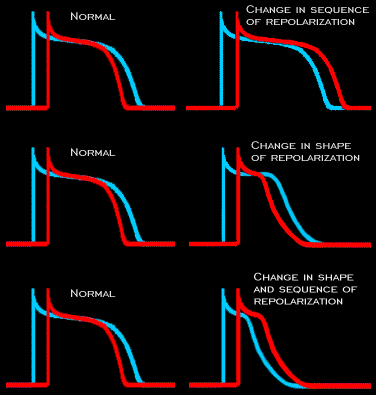
T wave abnormalities result from changes in the in the sequence of repolarization and/or changes in the shape of the repolarization limb of the action potential. Both of these changes will cause changes in the magnitude and the direction of the voltage gradients created during repolarization.
