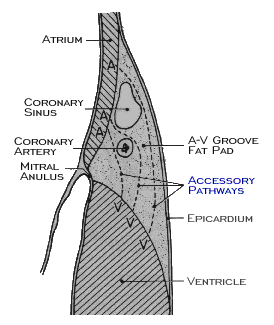
Conduction across the AV junction may also be accelerated, causing shortening of the PR interval to less than 120 ms. This may be due to accelerated conduction within the AV node itself, considered to represent one end of the normal physiologic spectrum, or to conduction across the AV junction via a tract or tracts of myocardial tissue, known as Kent bundles that bypass the AV node, These AV nodal bypass tracts are also referred to as accessory pathways and may span the AV ring at a variety of locations. Impulses conducted to the ventricles via these pathways activate the ventricles abnormally and cause intra-ventricular conduction disturbances with characteristic ECG features. These are discussed in greater detail in the next chapter.