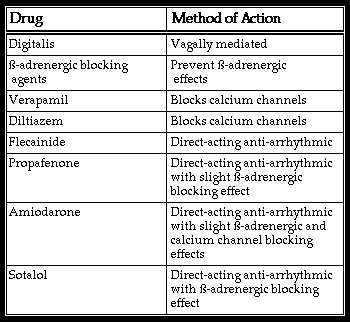
A variety of drugs, some of which are listed here, will slow conduction through the AV junction and cause prolongation of the PR interval. These include digitalis, whose effect on the AV junction is believed to be vagally mediated, the beta-adrenergic blocking agents which block beta-adrenergic effects on the AV node leaving parasympathetic effects unopposed, and the calcium channel blocking drugs which directly block the slow, calcium-dependent inward current in the upper portion of the AV node. Direct acting anti-arrhythmic drugs such as amiodarone and class 1C drugs such as flecainide and propafenone also slow conduction through the AV junction and lengthen the PR interval.