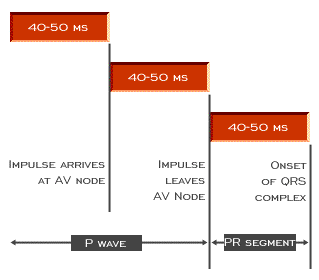
The impulse reaches the AV node at about the same time it arrives at the left atrium. This occurs when the first half of the P wave,i.e. the right atrfial component, has been inscribed, and this occurs about 40-50ms after the onset of the P wave. It takes about 50 ms for the impulse to travel through the AV node, exiting at a time that is roughly coincident with the end of the P wave (which is normally about 100-120 ms in duration) and about 40-50 ms prior to the onset of the QRS complex.