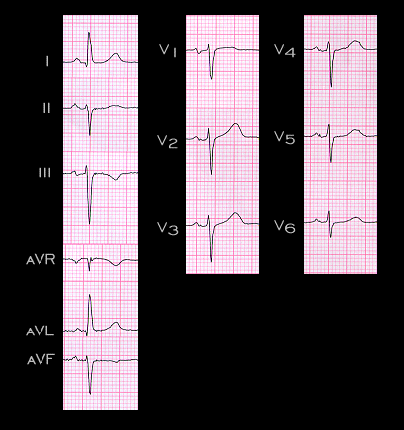
Other causes of poor R wave progression include: 1. Left anterior fascicular block. 2. Chronic obstructive airway disease. 3. The relationship between the position of the chest electrodes and the position of the heart. The ECG shown here is from a 78 year old woman with left anterior fascicular block and poor R wave progression in the V leads. There was no prior history or clinical evidence of coronary artery disease.
