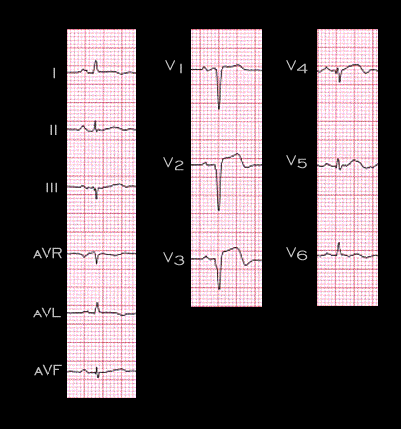
As indicated earlier, the presence of Q waves or QS complexes in leads V1, V2, and V3, as shown again in this tracing, permit the diagnosis of an infarction involving the interventricular septum and the anterior left ventricular wall with a reasonably high degree of accuracy. However, the interpretation of the ECG with QS complexes in only V1 and V2 or with a small R wave in leads V1-V4 is more difficult.
