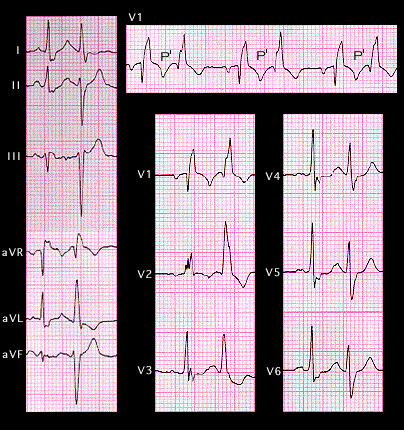
If one portion of the conducting system has a fixed block, an early premature response may find a second fascicle blocked resulting in bifascicular block. The ECG shown here demonstrates atrial bigeminy. The premature P wave (P’) is difficult to see but is contained within the T wave of the non-premature beat. There is a repetitive long-short, long-short variation in cycle length. The first beat of each pair, the non-premature beat, conducts with right bundle branch block and a normal frontal plain main axis. The second of the pair, the atrial premature beat, also shows right bundle branch block, but now, the frontal plane main axis has shifted to the left, indicating the additional development of left anterior fascicular block. Try to draw the frontal plane spatial vectors and the encompassing vector loops for the non-premature and premature beats.
