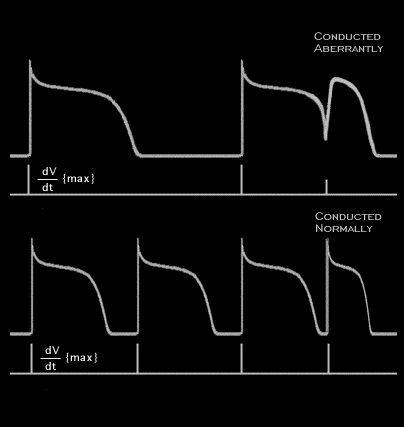
In the figure shown here, the last beat in both the upper and lower panels is premature and their coupling intervals are the same. In the upper panel, the basic rate is slower than in the lower panel. As a result, the duration of the non-premature action potentials is greater than in the lower panel, where the basic rate is faster. Because of this, the premature action potential shown in the upper panel arises from an incompletely repolarized fiber and a membrane potential that is less negative than the resting potential. Its upstroke velocity is reduced because of the voltage dependency of the sodium current and it will conduct aberrantly. The premature action potential in the lower panel, where the basic rate is faster, arises from a completely repolarized fiber. Its upstroke velocity is not reduced and it will conduct normally, without aberration.
