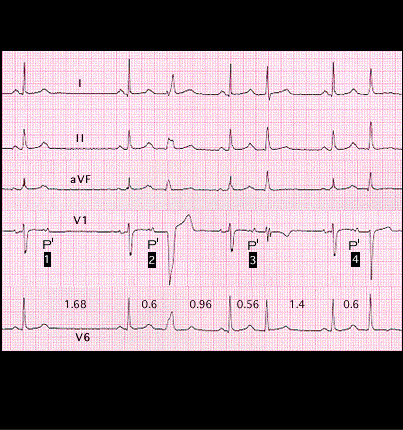
This ECG, from a different patient, demonstrates that whether or not an atrial premature beat conducts aberrantly depends not only on the RR interval of the premature beat, but also on the RR interval of the preceding beat. The ECG show a run of atrial bigeminy in which the first atrial premature beat (P’ 1) is blocked and does not conduct to the ventricles. The other atrial premature beats (P’ 2, P’ 3 and P’ 4) do conduct . Note that the type of aberrancy varies, resulting in premature QRS complexes with differing morphologies even though the coupling intervals of the premature complexes are nearly the same (0.6, 0.56 and 0.6 seconds). However, the RR intervals between the QRS complexes that precede the aberrantly conducted premature beats vary significantly (1.68, 0.96 and 1.40 seconds). It is the combined effects of the changes in preceding cycle length and the slight differences in the coupling interval of the premature beat that account for the different types of aberrancy.
