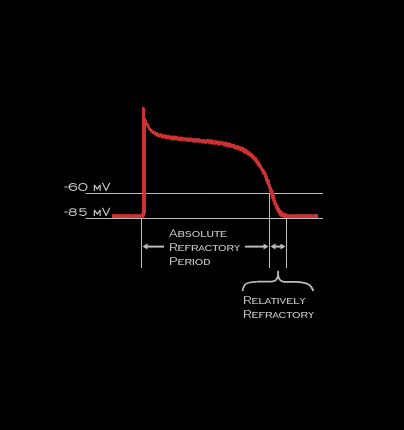
In normal ventricular fibers, the duration of the refractory period is determined primarily by the time required for the repolarization limb of the action potential (phase III) to return to -60 mV because the fiber is inexcitable, i.e. is absolutely refractory, until this transmembrane voltage is reached. Between transmembrane potentials -60 mV an -85 mV, the fiber will be incompletely recovered, i.e. will be relatively refractory. A response initiated during this time will be associated with action potentials having a decreased upstroke velocity. This will result in a decreased conduction velocity of the propagated response and is the mechanism most responsible for the aberrant conduction associated with early atrial premature beats.
