Type I SA block with Wenckeback periodicity produces group beating similar to that which occurs with type I AV block. However, with SA block the PR intervals are constant and the progressive slowing of SA conduction which culminates in SA block, must be deduced from analysis of the body surface ECG.
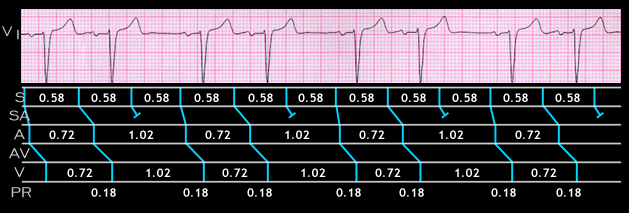
The ECG shown here is from a 72 year old male who was receiving diltiazem, a calcium channel blocking agent. The P waves are uniform in shape and their PR intervals are constant (0.18 sec). Note that the interval between each group of two (1.02 seconds) is less than twice the preceding RR interval (2 x 0,72 = 1.44 seconds). These features suggest type I block with Wenckeback periodicity and a 3.2.conduction ratio. As noted, the PR intervals are constant and there are no P waves during the pauses. This indicates that the conduction block is between the sinus node and the atrium rather than between the atrium and the ventricles. An alternative but less likely interpretation might be that the groups of 2 are caused by atrial premature beats in a pattern of bigeminy with the ectopic atrial focus located in close proximity to the sinus node. In this situation, the configuration of the premature ectopic P wave will be similar to that of the sinus P wave because the sequence of atrial activation will similar.
