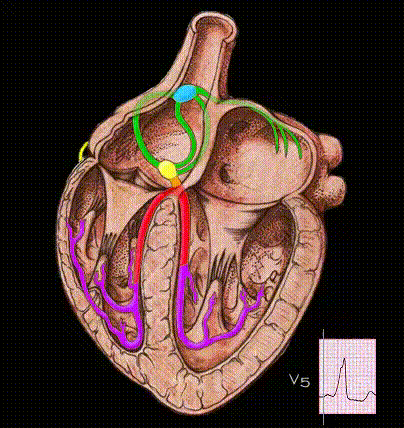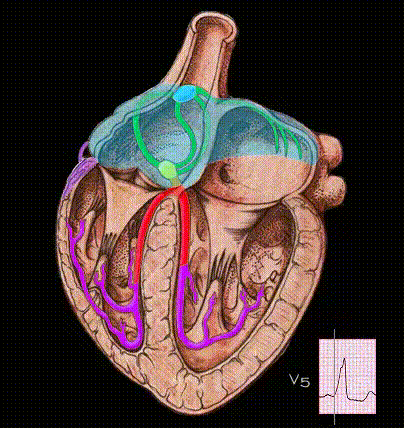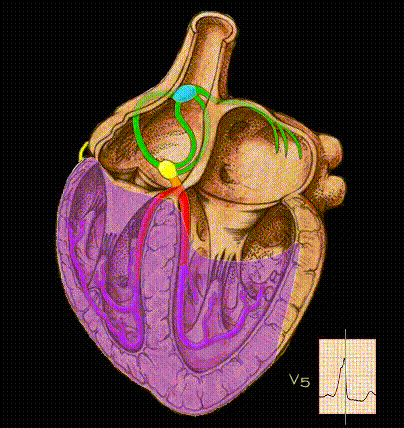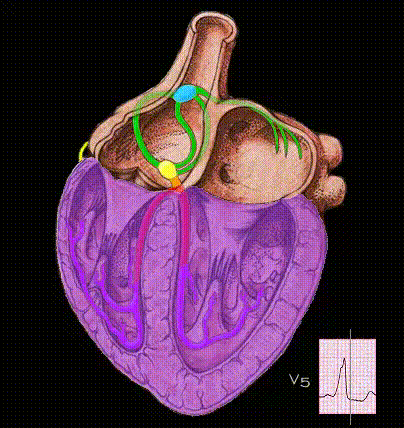
Here, the ventricles are activated entirely by an impulse traveling over the accessory pathway. Because conduction through the bypass tract is faster than through the AV node and because the ventricles are activated abnormally, the PR interval is very short and the QRS complex is abnormal in both its morphology and its duration.
