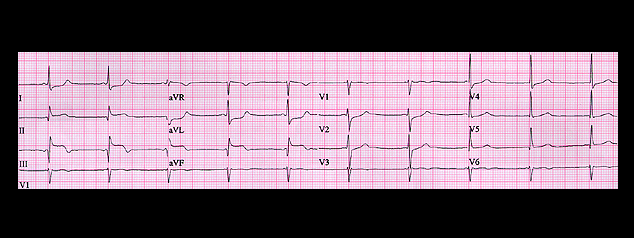
The P waves are difficult to identify. They precede each QRS complex with a short PR interval (0.10 seconds) and are flat in leads II and aVR, inverted in leads III and aVF and upright in leads I and aVL. This yields a P wave frontal plane spatial vector that is oriented to the left and superiorly with an axis of -30 degrees, consistent with an AV junctional rhythm with retrograde P waves. Now note that the ST segment is more elevated in lead III than in either lead II or aVF and is depressed in leads I and aVL. Its spatial vector is oriented to the right as well as inferiorly, suggesting the possibility of right ventricular involvement (which would help to explain the hypotension). In this patient, right sided chest leads should be employed to determine if there is ST elevation in leads overlying the right ventricle.
