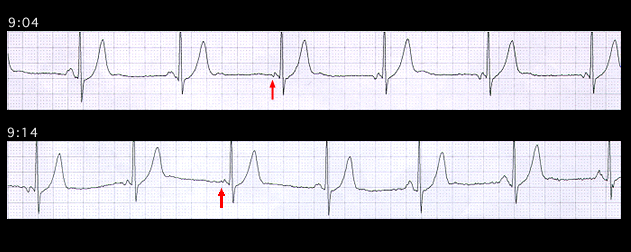
The ambulatory ECGs shown on this and on the next page illustrate an ectopic atrial rhythm (this page) and an AV nodal rhythm (next page) in the same 70 year old patient who was receiving verapamil, a calcium channel blocking agent, for control of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. The first two beats in this tracing are sinus. Thereafter, the P wave morphology changes, reflecting the emergence of ectopic atrial focus which is isorhythmic with the sinus. This rhythm persists for 10 minutes and then reverts to sinus rhythm when the sinus rate slightly exceeds the ectopic rate. Note that the P waves marked with an arrow are intermediate in shape between the sinus and ectopic P waves. They represent the fusion of the depolarizing wave fronts originating almost simultaneously from the two foci.
