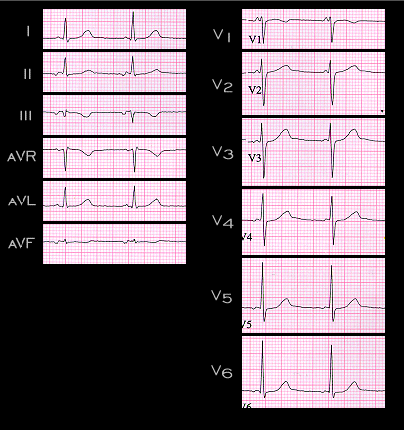
An ectopic focus located in the AV node but above the region responsible for most of the AV nodal conduction delay will depolarize the atria in a retrograde, superiorly oriented direction, before the impulse is able to travel through the conducting system to depolarize the ventricles. The PR interval associated with this superiorly directed P wave will usually be shorter than that associated with a sinus P wave or a P wave originating from an ectopic focus located in the atria. The ECG shown here was recorded from the same patient whose ECG from a different time was shown on page 7.2.2. Note that in this ECG, the P wave is inverted in leads II, III and aVF, and slightly positive in lead aVR and that in lead V1, the only obvious component is positive. Note also that the PR interval is 100 ms and that the end of the P wave almost merges with the onset of the QRS complex. Before going to the next page, determine the frontal plane axis of this P wave and compare it to that of the P wave shown on page 7.2.2.
