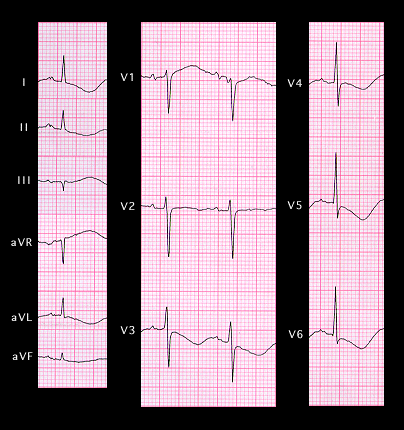
Inverted giant T waves with QT prolongation also occur in patients with an intracranial hemorrhage and other lesions associated with an increase in intracranial pressure. In these settings, it is referred to as the “CVA pattern.” This is illustrated in the ECG shown here, recorded from a 67 year old female following a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Note the deeply inverted T waves and the prolongation of the QT interval. Occasionally, similar T wave changes may be seen after extracranial manipulation of the autonomic nervous system such as may occur with radical neck dissections.
