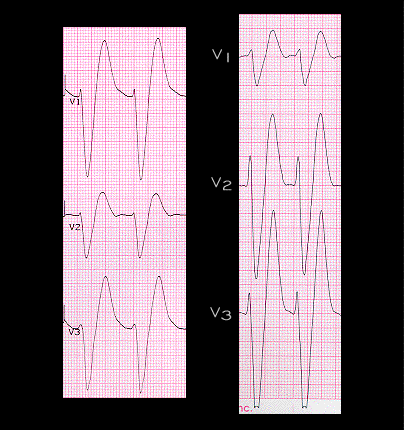
The diffuse widening of the QRS complex caused by the tricyclic (the tracing on the left) is similar to that caused by hyperpotassemia (the tracing on the right, recorded from a patient whose serum K was 7.7 mM). With the tricyclics, the QRS widening reflects the decrease in sodium conductance that occurs as a result of the drug binding to the sodium channel. With hyperpotassemia, the widening of the QRS complex reflects the decreased availability of the sodium channels that results from the decrease in resting membrane potential to less negative values.
