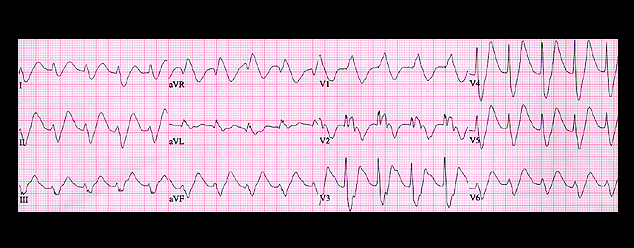
The ECG is an example of severe hyperpotassemia. Sinus P waves are present before each QRS but they are difficult to identify because they are broad and of low amplitude and are located on the downslope of the T wave. They are best appreciated in leads 2 and V3. The PR interval is prolonged (0.24 seconds) and the QRS complex is diffusely widened, measuring 0.20 seconds. In addition, there are peaked T waves. The QRS configuration suggests right bundle branch block with left axis deviation. You should recognize this combination of ECG features as indicative of severe hyperpotassemia, and in this patient, the serum K concentration was 8.8 mM.
