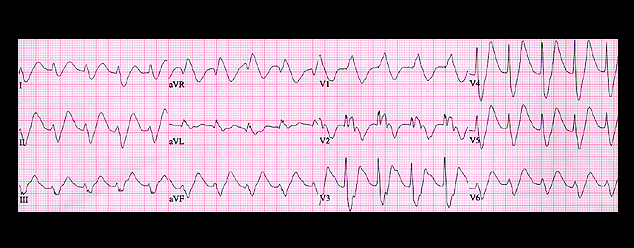
This ECGis from a 64 year old male with cirrhosis of the liver, portal hypertension, ascites and edema who was receiving spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist, as part of his diuretic management. He presented to the Emergency Department complaining of weakness and confusion. How would you interpret this ECG?
