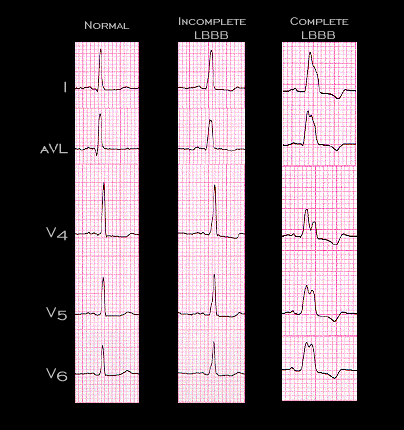
Presented side-by-side for comparison are the normally conducted beat, the beat conducted with incomplete left bundle branch block and the beat conducted with complete left bundle branch block. Note once again, the changes in both the duration and morphology of the QRS complex, and the changes in the ST segment and T wave that occur with the development of the conduction disturbance.
