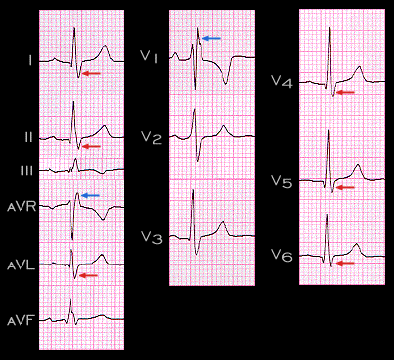
The ECG shown here illustrates the typical electrocardiographic features of complete right bundle branch block. It is important to note that because impulse transmission through the left bundle is unaffected, the initial part of the QRS complex, i.e. a small Q wave in leads II and III and a small R wave in leads aVR and V1, which reflect the normal left-to-right depolarization of the interventricular septum is unchanged. The main portion of the QRS complex is also unchanged with R waves in leads I, II, aVF and V3-6 and S waves in leads aVR and V1. These reflect the normal sequence of left ventricular depolarization.
The unopposed right ventricular forces are represented by the broad S wave in leads I and V6, i.e. the left sided and posterior/inferior leads (the red arrows), and by the R’ in leads aVR and V1, i.e. the right sided, and anterior/superior leads (the blue arrows) . The duration of the QRS complex is prolonged and measures 0.12 sec.
