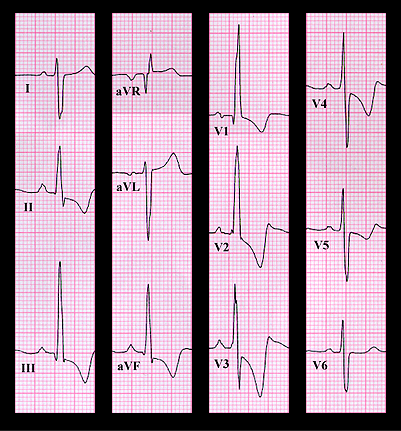
Her ECG is shown again here. The rhythm is sinus and the PR interval is normal. The QRS duration is slightly prolonged (at least 0.10 seconds) and the frontal plane QRS axis is +120 degrees. This is abnormal right axis deviation. The qR complex in lead V1 with the tall R wave (28mm or 2.8 mV), the S wave of greater amplitude than the R wave in leads V5 and V6 and the deeply inverted T waves in leads V2-V5, combined with the right axis deviation, are indicative of right ventricular hypertrophy and suggest that the right ventricular systolic pressure equals or exceeds left ventricular systolic pressure. The ECG is consistent with either severe pulmonic stenosis or pulmonary hypertension. The characteristics of the murmur, combined with the ECG, suggest a diagnosis of severe pulmonic stenosis. This diagnosis was confirmed by cardiac catheterization. The systolic pressure in the right ventricle was 164mm Hg while that in the left ventricle was 124mm Hg.
