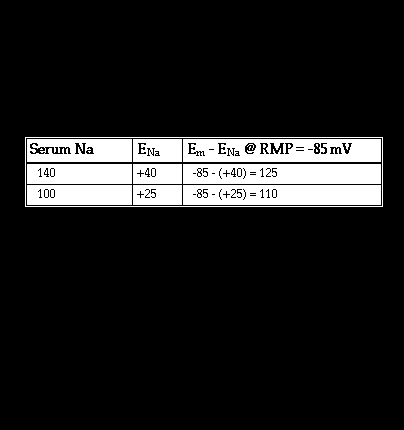
Clinically encountered changes in serum sodium do not alter the electrocardiogram in spite of the role of the sodium inward current in generating the upstroke of the action potential and, by extension, the QRS complex on the electrocardiogram. For instance, a decrease serum sodium from its normal value of 140 mM to 100 mM will change the sodium equilibrium potential, as determined by the Nearnst equation, from + 40 mV to +25 mV (see page 5.1.2). and will decrease the electrical driving force for sodium from 125 to 110 mV when the resting potential is -85 mV. This change will cause only a slight decrease in the maximum rate of rise of the action potential upstroke and no significant effect on the QRS complex of the electrocardiogram.
