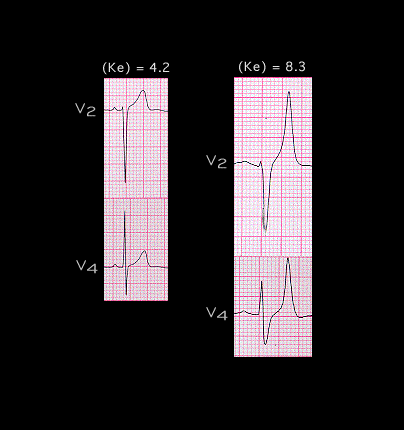
As potassium rises further, conduction slows in the atria and ventricles causing the P wave and QRS complex to widen. There is sometimes a shift in the QRS axis as well, implying that the conduction slowing may be more pronounced in some portions of the conducting system than in others. The T wave remains peaked and symmetrical, giving it a tented appearance.
