QT prolongation may be acquired or congenital, and when associated with ventricular arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation are referred to as the acquired and congenital long QT syndromes. The acquired causes of QT prolongation are, as has been discussed in this chapter, those associated with electrolyte abnormalities, cardioactive drugs, particularly the type Ia and III antiarrhythmic drugs,as well as a variety of other drugs which affect the potassium and calcium channels, bradycardia and hypothermia.
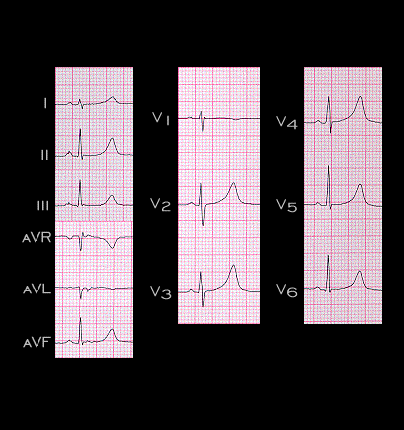
The tracing shown here is from a 15 year old girl with a history of unexplained syncope. The QT interval is 500 ms in duration and appears even longer in some leads. It simulates the electrocardiographic changes associated with hypocalcemia and hypothermia. However, this patient had neither hypothermia nor hypocalemia. This is an example of the congenital long QT syndrome, a disease that is due to a variety of chromosomal abnormalities in the genes that regulate the potassium and sodium channels and that is associated with ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation.
