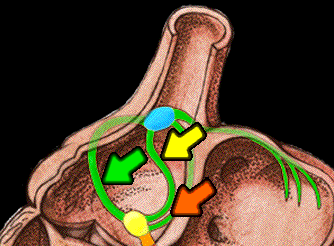
The sinus node is in direct continuity with the atrial musculature and with specialized atrial tracts which connect the sinus and atrio ventricular nodes as well as the right and left atria. The cells which comprise the anterior, middle and posterior internodal tracts appear to be morphologically distinct and conduct more rapidly than those of the normal atrial myocardial fibers. These tracts are not insulated from the remainder of the atrium and their functional role is unclear. It is possible that they facilitate conduction of impulses from the sinus node to the atrio ventricular node and in this way synchronize the arrival of the impulses to the atrio ventricular (AV) node.
