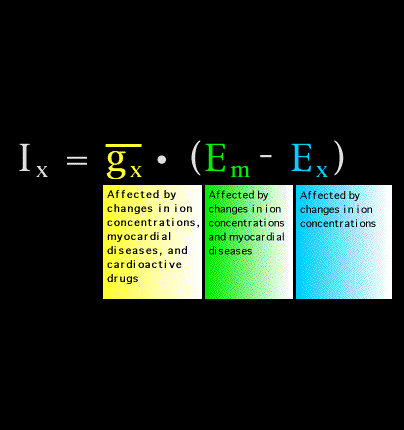
Changes in extracellular and intracellular ionic concentrations can affect ionic conductance, the resting membrane potential and the equilibrium potential for the various ions. Cardiac diseases such as ischemia, infarction and fibrosis can influence ionic conductance and resting membrane potential and cardioactive drugs, such as the direct acting antiarrhythmic agents can (and do) affect ionic conductance.
