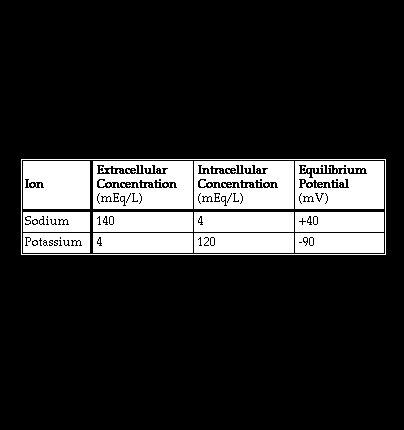
The equilibrium potential for a given ion (Ex) is the transmembrane voltage required to maintain the normal ratio between the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of that ion. It is expressed by the Nernst equation: Ex = -61 (log Xi/Xe) where Xi is the intracellular concentration and Xe the extracellular concentration of the ion. The intracellular and extracellular concentrations and equilibrium potentials for sodium and potassium are shown here.