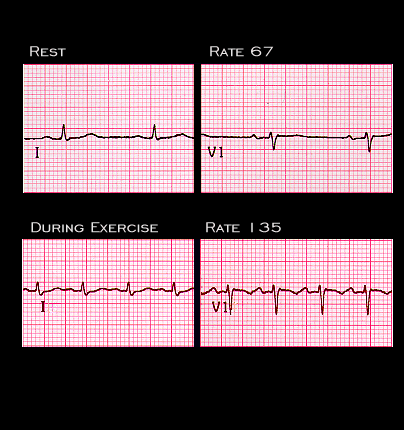
Sinus tachycardia is caused by an increase in the rate of spontaneous diastolic depolarization in the sinus node. The ECG shown here illustrates the development of sinus tachycardia during exercise. In most cases, sinus tachycardia is the physiologic response to factors that increase beta-sympathetic activity. Examples include not only the sinus tachycardia associated with exercise, as shown here, but also that which occurs with stress and anxiety, fever, anemia and hyperthyroidism. Sustained sinus tachycardia, occurring even at rest, should trigger a search for the underlying cause.
